DEFORESTATION : CAUSES AND CONSEQUENCES
Deforestation is the phenomenon of forest areas reduction. We talk about deforestation when forest areas are definitely lost for uses such as agriculture, urbanization or mining activities. Our foundation Free Spirit wants to raise awareness of massive deforestation.

ABOUT THE CURRENT SITUATION
Today, 30% of the planet is covered with forests whereas this figure represented 66% 400 years ago. According to World Resources Institute, 80% of the world original forest area was cut down or degraded, essentially during the last 30 years…
Between 1990 and 2000, each year, it was more than 14 million of forests hectares which disappeared each year. From 2000 to 2012, we talk about more than 23 million of hectares. In total, since 1990, the world has lost in forest, the equivalence of the South-Africa area, meaning 129 hectares. Finally: during the period from 2010 to 2015.
A sad record was registered in 2016 with a loss of 30 million hectares of forests.
Today, each year, the equivalence of Greece area disappears.
CAUSES
The disappearance of forests can be due to Men activity or to natural phenomenons such as fires, diseases which could affect trees.
Man is however the 1st responsible.
However, regardless the received ideas, the forest industries are not among the main responsible of deforestation. The companies of this industry exploit culture forest areas more often: some forests regularly replanted so that they can be exploited sustainably.
Oil and gas extraction affects considerably forest environments. These are damaged by pipeline constructs, drillings. Forests provide with wood-energy, used by households in individual fireplaces, collective heating for urban heating, industry and agriculture.
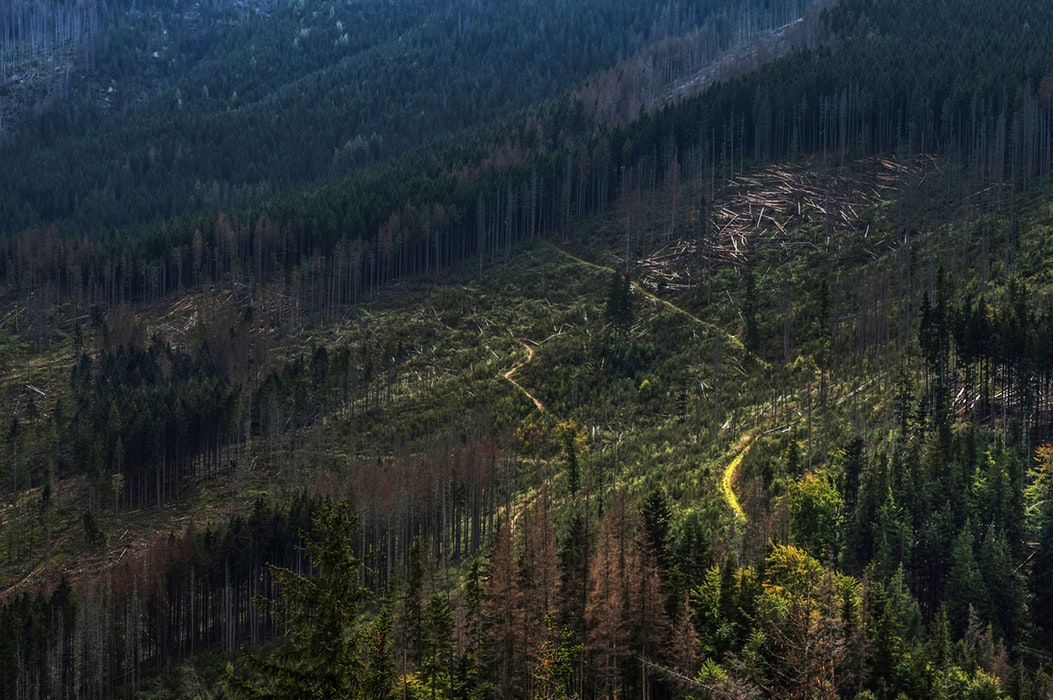


Based on the report on the World Forest State published by the FAO in 2016, about 80% of the deforestation in the world is caused by agriculture (the remaining 20% is divided between the infrastructure construction, urbanization and mining activities). However, the agricultural expansion remains the main cause of forest clearing in the world : planting oil palm trees, developing the culture to feed the farm animals, mining minerals and metals exploitations. Some forests are cut down for their palm oil, to cultivate soya which feeds the cattle or to cultivate sugar cane. Finally, the demographic growth is also one of the agricultural expansion causes. As far as agricultural expansion is concerned :
- Agriculture business represents 45 to 50%
- Local peasant agriculture represents 30 to 35%
- Breading represented 15%
Finally, illegal exploitation also plays an important role in the planet – deforestation. In Europe, we estimate that a quarter of wood importation is considered as from illegal origin. The research from Interpol estimates that between 50 and 90% of the forest exploitation in the tropical countries are illegal exploitations.
Deforestation and palm oil
Palm oil production, more and more reported, is one of the most important causes of deforestation in some regions of the world. According to the FAO, palm oil industry has been a huge factor in deforestation. Thanks to the pressure of some NGOs, of new regulations and consumers, the palm oil sector begins to be normalized after having known a huge number of illegal forest exploitations. This industry can be also a real environmental problem.

CONSEQUENCES
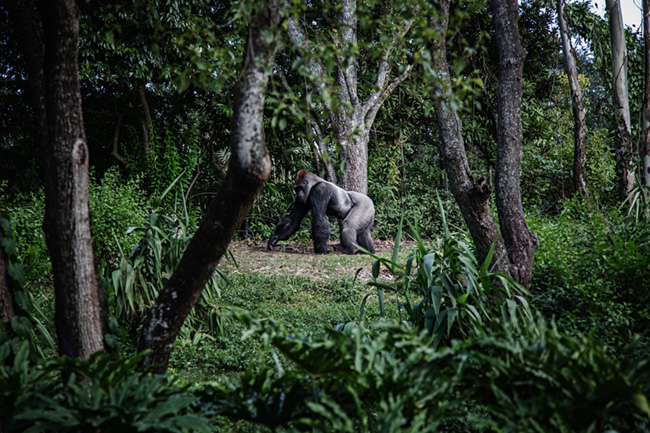

BIODIVERSITY LOSS
Forests cover 80% of terrestrial biodiversity. It is a real haven for animal and plant species. The forest shelters mammals, birds, insects, amphibians and species often rare and fragile. Deforestation is thus a disaster not only for Men but also for all lives on Earth. One of the biggest dangers : the biodiversity loss can be irreversible. Many species are threatened with extinction because of forests disappearance. For example, the bigs apes in Africa, see their number tremendously diminish because of the destruction of their natural habitat.
INCREASING DISEASES
According to the Institute of Research for the Development (IRD), forests diminish infectious diseases. The deforestation remains one of the main causes of the emergence of new infectious agents and their epidemic movement in the human populations. According to a study, 40% of the world population lives in regions affected by malaria. Yet, in the areas zones highly deforested, the risk of contracting this disease is 300 higher than in the forest areas.
72% of the emerging diseases transmitted by animals to Men are spread by wild animals. Deforestation encourages the contact between Men and animals and encourages thus the transmission of pathogens agents.
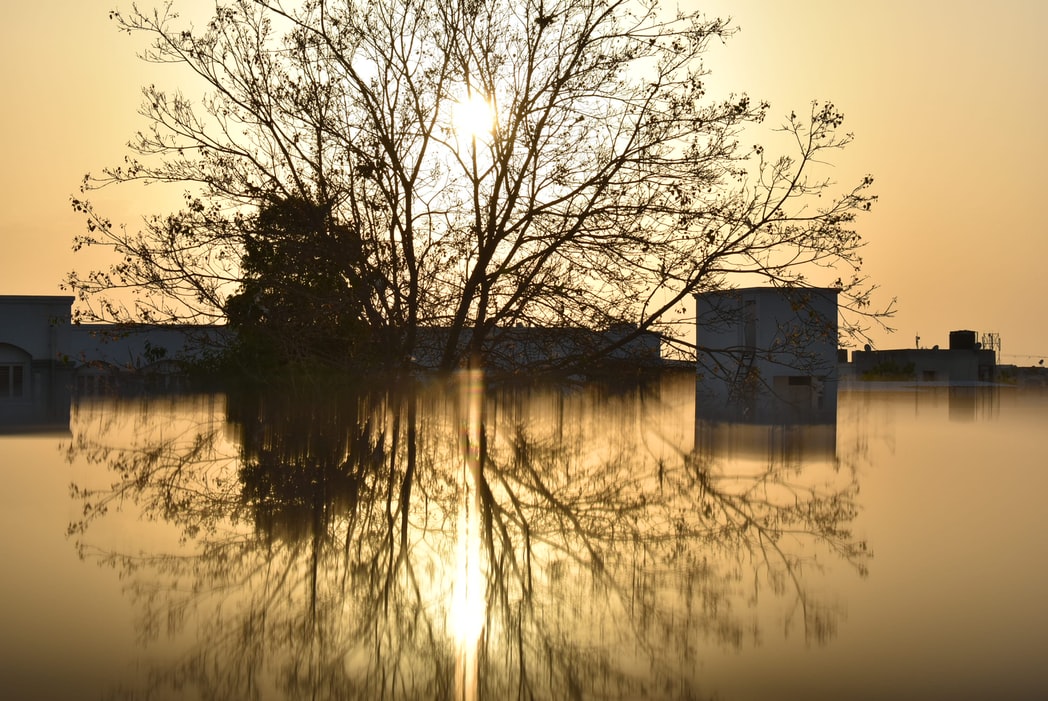

NATURAL DISASTERS
Forests are essential to the structure and the soil quality. Indeed, they diminish the hydric and wind turbine erosion and maintain the cycle of nutrients in these soils. A bared soil does not bring the essential protection anymore against violent rains. Environment becomes then more favorable to landslide and flooding. Haïti for example, where more than 90% of trees were cut down, keeps suffering from deadly mudslides because water is not kept anymore by the roots in the localities localized on sea level. In others regions of the world, particularly affected by deforestation and where hurricanes commonly happen, forests are not natural barriers anymore to protect against tsunamis and cyclones.
CLIMATE CHANGE
A study from Leeds university (Great-Britain) led by Dominick Spracklen showed that deforestation participated in reducing air humidity.
Furthermore, the massive forests disappearance strongly participate in greenhouse gas, which is the cause of global warming. Deforestation is directly responsible for 17% of world carbon emissions. It is the 3d emitter after the energetic supply and et industry.
Forests are carbone vessels. They hold it both in the live and dead biomass, in the decaying organic materials and in soils. Huge quantities of carbone have been released in the atmosphere because of the deforestation. In 2005, forests kept more than the half of carbone accumulated by terrestrial ecosystems.
Finally, according to the experts from IPCC pour Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change , regarding futur global warming, from +2°C, the terrestrial ecosystems risk to release more greenhouse gas in the atmosphere and they will not store it.
WEAK SOIL
Deforestation weakens soils. The forest makes soils richer in terms of organic matter and makes them more resistant to bad weathers and erosions. Thus, when a forest is destroyed, the soil is weakened and becomes more vulnerable to natural disasters (landslip).
DIMINUTION OF WATER
For drinking water, the forest helps to replenish the water tables. ¾ of drinking water comes from forested catchment areas. ⅔ of big cities of developing countries depend on forests for their drinking water supply The forest which filters and holds water, protects against catchment areas which provide purified fresh water to rivers. Because of the deforestation, we are facing soils erosion and siltation of waterways. This leads to reduce access to drinking water.





